By Erin Stone
DMLS Matures from Rapid Prototyping to Production Parts
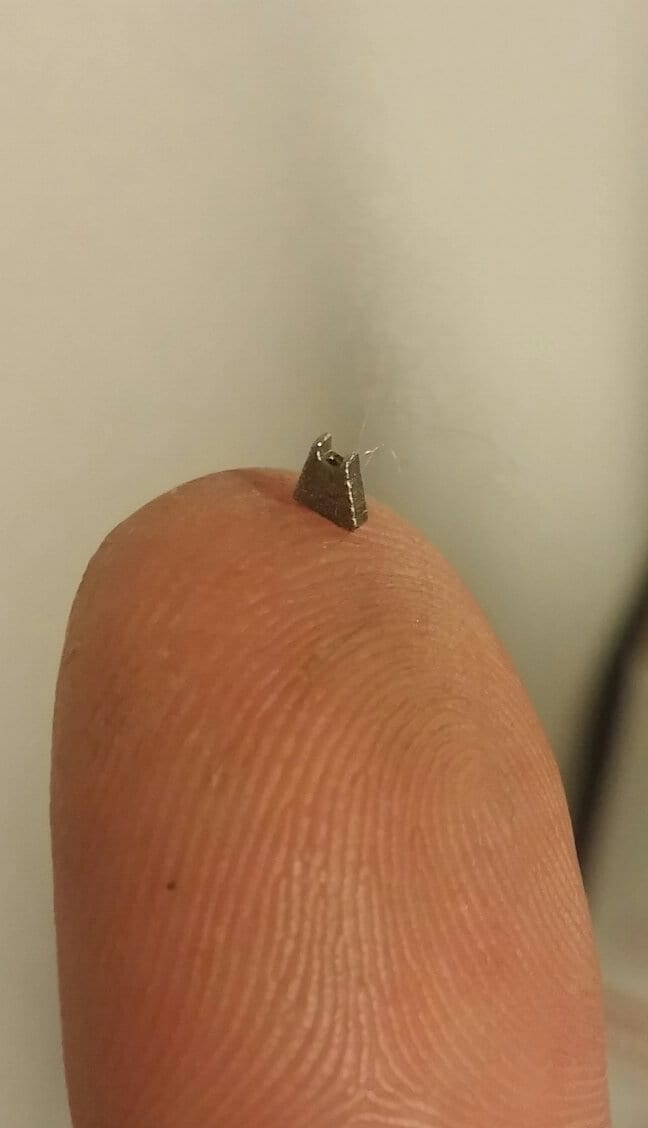
Direct Metal Laser Sintering (DMLS) 3D printing was featured first as an excellent rapid prototyping tool and then as a new manufacturing advancement in two 3D Printing Industry News items over the past two days. So which is it, prototyping or production parts? The fantastic news for designers, engineers, and production managers is that DMLS has been a phenomenal rapid prototyping tool for functional metal parts for years and now it is also a proven metal manufacturing method for complex parts ranging from turbines to heat exchangers.
DMLS Rapid Prototyping Saves Valuable Weeks of Development Time
As Scott Grunewald points out in his article, “This (DMLS) rapid prototyping allows newly developed components to be test installed, articulated and checked for clearance and movement tolerances. The final models can then be used to create the drawings and manufacturing guides that define construction materials, inspection requirements and post processing features. This portion of the process is so fast that the final part is just being completed by the time the approved drawing is released.” Innovations can be tested in working models, using titanium, inconel, tool steel, stainless steel or aluminum and then tweaked and retested in a matter of days. DMLS parts near 100% density, making them comparable or denser than machined or cast parts. 3D metal printing, like other 3D printing methods allows multiple 3D models to be built at the same time without contending with expensive CNC programming time. Aerospace giants like GE and Lockheed Martin have invested in hundreds of DMLS machine to take advantage of this competitive advantage.
DMLS is Now a Proven Manufacturing Method for Production Parts
While GE and other aerospace players have used 3D prototyping for years, they have also increasingly starting using DMLS for production runs. Sigma Components’s news about its funding and partnership with Rolls Royce to utilize DMLS to manufacture complex functional parts for use in end products highlights the untapped potential 3D manufacturing brings to production. DMLS has progressed in its speed and reliability to the point of becoming a viable process for Sigma to “…redesign and develop lightweight pipe end fittings that use 3D printing and additive manufacturing to reduce the weight of traditionally manufactured components and minimise part and manufacturing costs.” However, to achieve its full potential, designers and engineers must shift their perspective to Design-for-3D, eliminating traditional manufacturing design constraints.
i3D MFG™ is focused on helping its customers realize these manufacturing advantages. With a full team of 3D engineers, as well as its designation as the EOS Material Process Application partner, we not only offer 3D manufacturing, but new DMLS powder development, parameter development, and of course, rapid prototyping.
Like this:
Like Loading...